methylisothiazolinone scrutiny
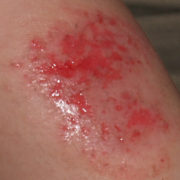
Methylisothiazolinone scrutiny is very much needed. This preservative is sensitizing a significant number of adults and children worldwide. It is found in personal products, household cleaners, household paint, and air fresheners. Reactions to it may look like atopic dermatitis!
“Recalcitrant dermatitis, such as that of the hands, face, or genitals, may be due to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) from ingredients in seemingly innocuous personal care products. Rising rates of allergy have been noted due to the preservative methylisothiazolinone (MI). This preservative is commonly found in skin and hair care products, especially wipes. This study evaluated the use of MI in products specifically marketed for babies and children and examined the associated marketing terms of such products. Ingredients of skin care products specifically marketed for babies and children were surveyed at two major retailers. Of 152 products surveyed, 30 products contained MI. Categories of products surveyed included facial or body wipes, antibacterial hand wipes, hair products, soaps, bubble baths, moisturizers, and sunscreens. Facial or body wipes and hair products were the categories with the greatest number of MI-containing products. MI-containing products were manufactured by a number of popular brands. Of note, products marketed as “gentle,” “sensitive,” “organic,” or “hypoallergenic” often contained MI, thus emphasizing the importance of consumer scrutiny of product choices. These findings reinforce the importance of educating parents and providing consumer decision-making advice regarding common skin care products, in order to help prevent ACD in children.” Learn more by clicking here: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4197884/.
It is time for methylisothiazolinone scrutiny – there is an epidemic! The Dermatitis Academy [www.dermatitisacademy.com] is tracking this epidemic and reporting new cases of methylisothiazolinone and new sources!!! It is important that consumers continue to let the Food and Drug Administration [FDA] know that they are known to be allergic to methylisothiazolinone and which product they have reacted to. Click here for information on FDA reporting: https://www.dermatitisacademy.com/methylisothiazolinone-page/